Ethiopia Volcano Eruption 2025: Shocking Blast Triggers Global Concern

Introduction: Africa Volcano Breaking News
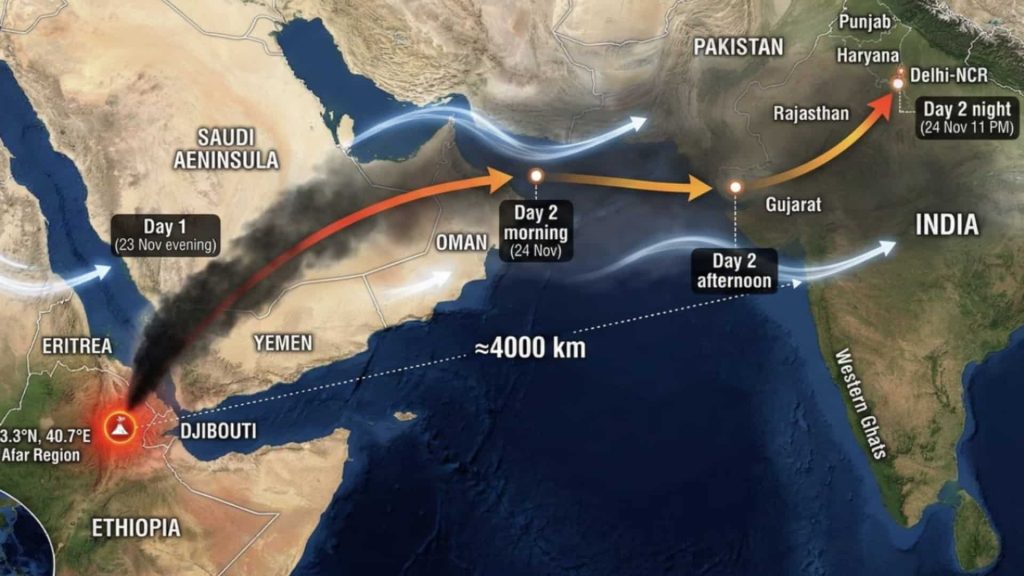
On 23 November 2025, the Ethiopia Volcano Eruption 2025 shocked scientists and the public when the Hayli Gubbi volcano erupting in Ethiopia’s Afar Region reactivated after 12000 years of silence. The eruption produced explosive ash emissions that climbed up to high altitudes and moved rapidly across borders. The ash crossed the Red Sea and triggered Yemen, Oman ash fall alert. Weather agencies also tracked the ash cloud reaching Pakistan, raising concerns about aviation safety and health risks. (The Guardian)
This event changed the scientific understanding of volcanic behavior in the Afar Rift. Researchers now study gas emissions, seismic activity, and satellite imagery to predict future activity. The eruption became a central topic in Africa volcano eruption today coverage and increased demand for accurate volcano eruption latest updates. (Wikipedia)
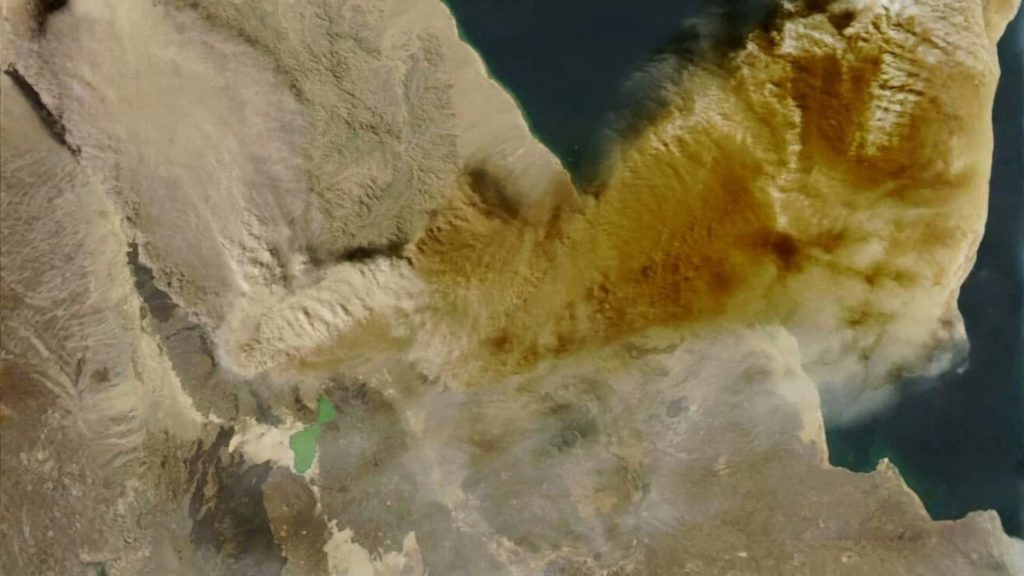

Table of Contents
Ethiopia Volcano Eruption 2025: Understanding
Location and Geology
The Hayli Gubbi volcano erupting is located in the Afar Region of Ethiopia, one of the most tectonically active rift zones in the world. This area forms part of the East African Rift System, where the African Plate is gradually splitting apart, creating volcanic activity and seismic events. (Al Jazeera)
- Hayli Gubbi belongs to the Erta Ale Range, a series of shield volcanoes in northeastern Ethiopia. These volcanoes are characterized by gentle slopes but can produce highly fluid lava flows that cover large areas.
- The volcano rises to an elevation of approximately 493 meters above sea level, situated in a remote, arid, and extremely hot desert landscape. These harsh conditions have historically made monitoring and research challenging, contributing to limited scientific records of activity.
- Its location in the Afar Depression makes it significant for Africa volcano breaking news, as eruptions here can have widespread regional impact.
Dormancy and Historical Context
The Hayli Gubbi volcano is classified as a 12000-year dormant volcano, meaning it had no confirmed eruptions during the Holocene.
- Geological surveys indicate that the volcano remained inactive for thousands of years, making the Ethiopia volcano eruption 2025 unprecedented in modern history.
- The long dormancy period explains why the eruption took both scientists and local populations by surprise.
- Because of its historical inactivity, volcanologists now study Hayli Gubbi closely to assess potential future activity, eruption patterns, and volcanic hazards.
- The eruption also emphasizes the importance of Ethiopia ash cloud update monitoring, as even long-dormant volcanoes can suddenly produce explosive activity. (Africa News)
Ethiopia Volcano Eruption 2025: Timeline and Characteristics
Onset of Eruption
The Hayli Gubbi volcano erupting came as a dramatic surprise on 23 November 2025 at 08:30 UTC. Early reports described initial explosive activity that propelled ash and volcanic gases high into the atmosphere, marking a rare event for a 12000-year dormant volcano.
- According to the Ethiopia ash cloud update, the volcanic plume quickly reached heights of 13–15 km, entering the stratosphere.
- Satellite imagery from Copernicus and the Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) immediately confirmed the eruption, tracking ash dispersion over the Red Sea and beyond.
- The eruption drew Africa volcano breaking news attention, highlighting the significance of monitoring even long-dormant volcanoes. (Geo News)
Eruption Type and Intensity
The 2025 eruption is classified as sub-Plinian, indicating explosive activity with high ash and gas output, but not a catastrophic eruption like a Plinian or supervolcanic event.
- Significant sulfur dioxide (SO₂) emissions were detected, suggesting that fresh magma had reached the surface, releasing volatile gases.
- The eruption produced pyroclastic material and a substantial ash plume that threatened nearby communities and affected regional air quality.
- Observations from Ethiopia volcano satellite images captured the ash drift patterns, allowing scientists to model plume trajectory and potential hazards.
Plume Movement and Spread
The eruption’s ash spread rapidly, with significant regional and transboundary effects:
- The ash moved eastward over the Red Sea, prompting Yemen Oman ash fall alert.
- High-altitude ash traveled thousands of kilometers, raising concerns about aviation safety and global weather impact Ethiopia volcano.
- Forecast models indicated minor ash impact over southern Pakistan, with concentrations too low to pose immediate ground-level hazards.
- The eruption’s plume is a critical case study for monitoring Africa volcano eruption today, illustrating how even a remote, long-dormant volcano can have far-reaching impacts.
Ethiopia Volcano Eruption 2025: Local Impact in Afar Region
Communities and Livelihoods
The Ethiopia Afar region eruption of Hayli Gubbi volcano erupting had immediate effects on nearby communities, particularly villages like Afdera. Heavy ash fall blanketed homes, roads, and local infrastructure, creating both health and logistical challenges.
- Herders faced contamination of grazing lands, putting livestock at risk and threatening the region’s pastoral economy.
- No fatalities have been confirmed, but infrastructure damage included ash-covered roads, rooftops, and storage facilities, disrupting daily life and local commerce.
- The eruption served as a stark reminder of the vulnerability of remote African communities to natural disasters, especially from a 12000-year dormant volcano that was previously thought inactive. (The Watchers)
Health and Environment
The eruption poses significant health and environmental risks, particularly from airborne volcanic ash:
- Respiratory hazards: Fine ash particles can irritate lungs and eyes, increasing risks of asthma and respiratory infections. Locals are advised to use masks and protective eyewear during ash fall.
- Water contamination: Ash settling into water sources can affect both humans and livestock, necessitating careful water management.
- Volcanic ash safety precautions: Residents are encouraged to stay indoors during heavy ash fall, regularly clean roofs to prevent collapse from accumulation, and avoid grazing livestock in areas with dense ash deposits.
Ethiopia Volcano Eruption 2025: Regional and International Impacts
Aviation Disruption
The Ethiopia volcano eruption 2025 had immediate effects on international aviation, drawing attention in Africa volcano breaking news outlets. The Hayli Gubbi volcano erupting produced a significant ash plume that posed serious risks to aircraft engines and flight safety.
- Airlines were forced to reroute or cancel flights, particularly over the Red Sea corridor, one of the busiest international air routes in the region.
- Volcano eruption latest updates provided guidance on safe flight paths, reducing the risk of engine abrasion or failure caused by fine volcanic ash.
- Satellite monitoring and advisories from the Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) ensured that aviation risks were mitigated effectively, demonstrating the importance of real-time volcanic monitoring for international air traffic safety.
Ash Cloud Across Borders
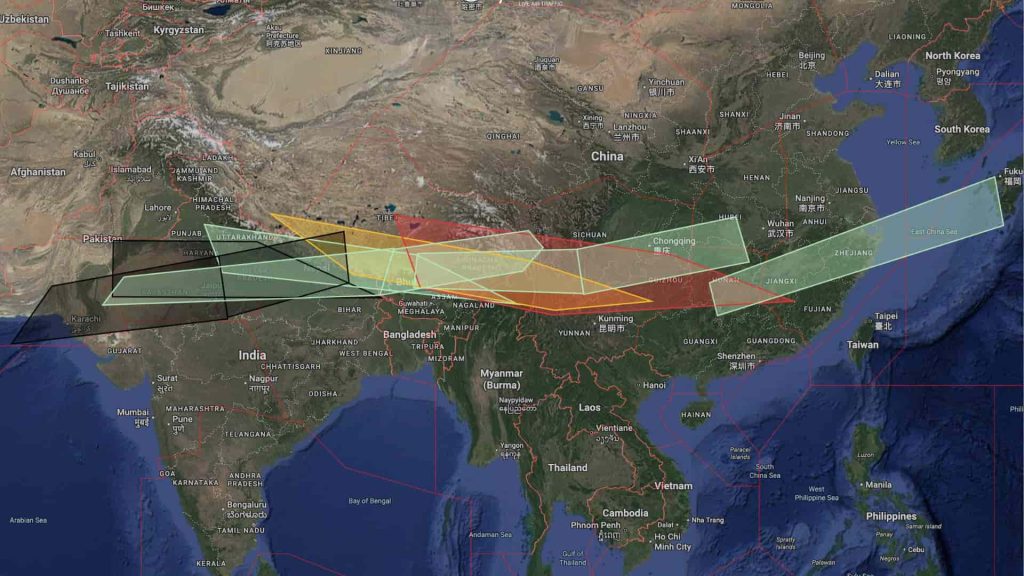
The eruption also caused transboundary effects, emphasizing the regional and international implications of volcanic activity:
- The ash traveled eastward, affecting Yemen and Oman, prompting ash fall alerts and public safety advisories.
- Meteorological authorities in Pakistan monitored the ash cloud reaching Pakistan, although concentrations were low and unlikely to cause major health or infrastructure issues.
- Neighboring countries, including India, adjusted air traffic and issued precautionary advisories, demonstrating coordinated Africa natural disaster news response efforts.
- The event highlights how a single eruption of a 12000-year dormant volcano in Ethiopia can have effects thousands of kilometers away, impacting air travel, public health, and regional weather. (The Watchers)
Ethiopia Volcano Eruption 2025: Scientific Significance
Rare Geological Event
The Hayli Gubbi volcano news from the Ethiopia volcano eruption 2025 offers an unprecedented opportunity to study a 12000-year dormant volcano coming back to life. This rare geological event provides critical insights into volcanic behavior in one of the most active tectonic regions of Africa, the Afar Rift.
- The sudden eruption challenges long-held assumptions that long-dormant volcanoes pose minimal risk, emphasizing the need for continuous monitoring.
- Gas emissions, lava flow patterns, and satellite data collected during the eruption allow volcanologists to model potential future activity, predict eruption patterns, and assess hazards.
- Researchers can compare the current activity with historical eruptions in the Erta Ale Range to understand magma dynamics and regional tectonics. (Africa News)
Climate and Environmental Effects
The Hayli Gubbi volcano erupting also has implications for climate and environmental conditions in the region:
- Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and ash injection into the atmosphere can temporarily influence regional climate by reducing solar radiation and altering local weather patterns.
- Fine ash particles affect sunlight absorption and may cause slight cooling in surrounding areas, potentially affecting agriculture and daily life.
- Long-term monitoring is essential to understand both immediate and lasting environmental impacts, including soil deposition, water contamination, and ecosystem disruptions.
- The eruption highlights the broader significance of global weather impact Ethiopia volcano, showing how volcanic activity in Africa can affect regions far beyond its origin.
Ethiopia Volcano Eruption 2025: Global Implications
Aviation Safety
The Africa volcano eruption today continues to influence global aviation planning. Airlines and aviation authorities now include the Hayli Gubbi volcano erupting in daily risk assessments, especially for routes crossing the Red Sea and Arabian Peninsula.
- Flight planners rely on updated ash reports to avoid dangerous airspace
- The Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) provides international coordination for tracking ash
- Real-time satellite monitoring helps reduce engine damage risks
- Airlines adjust altitudes or reroute flights to maintain safety
This coordinated response shows how a single eruption in Ethiopia can affect air traffic thousands of kilometers away.
Health and Public Safety
Communities downwind of the eruption continue to face ash inhalation risks. Fine particles can irritate the lungs, skin, and eyes. Health authorities recommend simple protective steps to reduce exposure.
Guidelines include:
- Wearing masks and eye protection during ash fall
- Limiting outdoor activity when ash concentration increases
- Cleaning ash from roofs to prevent structural damage
- Protecting water sources from ash contamination
Residents in Yemen, Oman, and southern Pakistan who follow these steps face lower health risks. Meteorological updates related to Ethiopia ash cloud update remain important for public safety. (Wikipedia)
Disaster Preparedness
The eruption highlights weaknesses in regional disaster planning. Countries in the region depend heavily on rapid updates from scientific agencies and Africa natural disaster news networks.
- Early warning systems must improve to alert remote communities
- Cross-border communication between Ethiopia, Yemen, Oman, and Pakistan supports better response
- Aviation alerts require fast and accurate data sharing
The event proves that long-dormant volcanoes can reactivate. Governments and scientific organizations now understand the importance of stronger monitoring systems for future events. (Geo News)
Ethiopia Volcano Eruption 2025: Monitoring and Research
Satellite and Ground Observations
Scientists monitor the Ethiopia volcano eruption 2025 through a combination of satellite and ground-based tools. Ethiopia volcano satellite images provide real-time visuals of ash plume height and direction. These images help track how the ash spreads across the Red Sea and toward Yemen, Oman, and southern Pakistan. (The Guardian)
Seismic devices record ground vibrations that indicate magma movement. Gas analysis detects sulfur dioxide levels, which signal fresh magma reaching the surface. These methods allow scientists to predict changes in eruption intensity.
Continuous updates support public safety. Agencies issue every Ethiopia ash cloud update to inform aviation authorities, local communities, and emergency services. (Al Jazeera)
Scientific Studies
Researchers plan extensive field studies once conditions allow safe access. Teams will collect ash samples to study composition, grain size, and chemical content. This information helps scientists understand eruption style and magma sources.
Data from this event supports long-term research into volcanic behavior within the Afar Rift. It also helps refine models used to predict future eruptions in the region.
These studies contribute to understanding Africa volcano breaking news patterns and how similar eruptions may develop. The results will influence emergency planning and risk assessment for Ethiopia and neighboring countries. (Wikipedia)
Ethiopia Volcano Eruption 2025: Safety Measures and Recommendations
For Residents
- Stay indoors during ash fall.
- Use masks and eye protection.
- Avoid contaminated grazing areas for livestock.
- Clean roofs and water sources carefully to avoid structural or health hazards.
For Aviation
- Follow VAAC alerts and volcano eruption latest updates.
- Inspect aircraft after exposure to volcanic ash.
- Adjust flight schedules based on satellite-tracked plume movement.
For Governments
- Strengthen disaster management plans for eruptions.
- Provide public communication and health advisories.
- Fund research and monitoring for Africa volcano eruption today and other high-risk zones.
Conclusion
The Ethiopia Volcano Eruption 2025 marks a remarkable geological milestone: a 12000-year dormant volcano, Hayli Gubbi, reawakens, producing a massive ash cloud that spans the Red Sea and reaches neighboring countries. This event underscores the unpredictability of nature, the importance of scientific monitoring, disaster preparedness, and international coordination.
2025 has already revealed numerous extraordinary natural phenomena, earning attention in studies like 3I-ATLAS: Extraordinary Discovery Stuns Scientists, which highlights unusual geological and environmental events worldwide. The eruption combines rare geological activity, regional human impact, and transcontinental environmental significance. It reinforces the need to track Africa natural disaster news, protect communities, maintain aviation safety, and stay informed through updates on Hayli Gubbi volcano news, Ethiopia ash cloud update, and global weather impact Ethiopia volcano.
FAQ – Ethiopia Volcano Eruption 2025
Q1: What caused the Ethiopia Volcano Eruption 2025?
A: The eruption was caused by the Hayli Gubbi volcano, a 12000-year dormant volcano in Ethiopia’s Afar Region. Magma pressure built up over centuries, leading to explosive ash emissions and lava flows.
Q2: How high did the ash plume reach?
A: The Ethiopia ash cloud update reported that ash reached heights of 13–15 km, spreading across the Red Sea and affecting countries like Yemen, Oman, and even reaching Pakistan.
Q3: Which regions were affected by the eruption?
A: The Ethiopia Afar region eruption impacted nearby communities, while the ash cloud extended to Yemen, Oman, southern Pakistan, and parts of India, causing alerts and potential aviation disruptions.
Q4: Is the eruption dangerous to health?
A: Volcanic ash can irritate lungs, eyes, and skin. Volcanic ash safety precautions include wearing masks, staying indoors, avoiding contaminated water, and protecting livestock from grazing on ash-covered land.
Q5: How does this eruption impact global weather?
A: The global weather impact Ethiopia volcano includes temporary changes in sunlight absorption, minor temperature fluctuations, and potential disruption to regional climate patterns due to sulfur dioxide and fine ash emissions.
Q6: How are authorities monitoring the volcano?
A: Authorities use Ethiopia volcano satellite images, seismic monitoring, gas emission analysis, and real-time ash tracking to provide volcano eruption latest updates and ensure aviation safety.
Q7: Why is this eruption significant scientifically?
A: The Hayli Gubbi volcano erupting after 12,000 years provides a rare opportunity to study a long-dormant shield volcano, helping scientists predict future volcanic activity and understand geological behavior in the Afar Rift.
Q8: Where can I follow updates about the eruption?
A: Follow sources covering Africa volcano breaking news, Ethiopia ash cloud update, and local meteorological departments for the most accurate and timely information.
Author: Mubashir Razzaq
Explorer of strange happenings and unusual natural events. Mubashir covers extraordinary geological phenomena, volcanic activity, and other rare occurrences, providing readers with accurate and engaging insights into the world’s most intriguing events.




